Introduction to Stochastic Oscillator Strategy
Technical indicators form the cornerstone of modern trading. They provide traders with essential insights into market dynamics. Among these, the Stochastic Oscillator stands as a stalwart, aiding traders in spotting potential trend reversals and overbought or oversold conditions.
Understanding the Stochastic Oscillator
At its core, the Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares a particular closing price of an asset to its price range over a set period. This comparison is presented in the form of two lines: %K and %D. These lines oscillate between 0 and 100, offering a visual representation of market momentum. High readings signal overbought conditions, while low readings indicate oversold conditions.
Types of Stochastic Oscillators
As traders delve into the world of technical analysis, the Stochastic Oscillator stands out as a versatile and valuable tool for market analysis. While it’s crucial to understand the core principles of the Stochastic Oscillator, it’s equally important to explore the various types of Stochastic Oscillators available. These different variations can help traders refine their Stochastic Oscillator strategy and adapt to varying market conditions.
1. Fast Stochastic Oscillator
The Fast Stochastic Oscillator is perhaps the most common and widely used version of the Stochastic Oscillator. It is known for its responsiveness to short-term price movements. Here’s what sets it apart:
- Speed: The Fast Stochastic calculates the %K and %D values over a short look-back period, typically 14 periods. This results in more sensitive and frequent signals.
- Volatility: Due to its sensitivity, the Fast Stochastic is more prone to fluctuations and can generate signals that respond quickly to market changes.
- Overbought and Oversold Conditions: It identifies overbought and oversold conditions rapidly, potentially leading to earlier entry and exit points in trades.
The Fast Stochastic is well-suited for traders who prefer shorter timeframes and more agile trading strategies, such as day traders and scalpers.
2. Slow Stochastic Oscillator
In contrast to the Fast Stochastic, the Slow Stochastic Oscillator is designed to provide a smoother and more stable representation of price momentum. Here’s what distinguishes it:
- Smoothing: The Slow Stochastic adds an additional layer of smoothing to the %K and %D values, often by applying a three-period simple moving average (SMA) to each line.
- Lag: Due to the added smoothing, the Slow Stochastic is less responsive to short-term price movements. It’s better suited for capturing longer-term trends.
- Reduced False Signals: The Slow Stochastic is less prone to generating false signals compared to its faster counterpart, making it suitable for swing traders and those who prefer a more relaxed trading approach.
The choice between the Fast and Slow Stochastic Oscillators depends on a trader’s preferred timeframe and trading style. While the Fast Stochastic excels in agility, the Slow Stochastic provides a more stable and reliable signal.
3. Full Stochastic Oscillator
The Full Stochastic Oscillator is an extended version of the Slow Stochastic, offering additional flexibility and customization options. Key features include:
- Customizable Look-Back Periods: Traders can adjust the look-back periods for both %K and %D, allowing for a broader range of analysis possibilities.
- Enhanced Precision: The Full Stochastic provides more granular insights into price momentum by allowing traders to fine-tune the indicator’s parameters.
- Flexibility: It can be applied to various timeframes and markets, making it adaptable to different trading strategies.
The Full Stochastic Oscillator is favored by traders who appreciate a high degree of customization in their analysis. It’s particularly useful for those who want to align the indicator closely with their unique trading goals and preferences.
4. Slow Stochastic with Smoothing (Smoothed Stochastic)
The Smoothed Stochastic, as the name suggests, further emphasizes smoothness in its signals. It achieves this by adding additional smoothing components to the traditional Slow Stochastic. Key characteristics include:
- Exceptional Smoothness: The Smoothed Stochastic is designed to reduce noise and produce exceptionally smooth %K and %D lines.
- Minimized False Signals: By reducing abrupt changes in indicator values, the Smoothed Stochastic aims to minimize false signals, making it suitable for traders who prioritize signal reliability.
- Enhanced Trend Identification: Its smoothed nature is particularly useful for identifying trends, and it’s often employed by trend-following traders.
The choice of Stochastic Oscillator type should align with a trader’s specific trading strategy and risk tolerance. While each type has its merits, understanding their differences is crucial to tailor your Stochastic Oscillator strategy effectively.
Role of Stochastic Oscillator in Trading
Understanding the Stochastic Oscillator
Before we explore its role, let’s briefly recap what the Stochastic Oscillator is. It’s a momentum indicator that measures the speed and change of price movements. This indicator generates two lines, %K and %D, which oscillate between 0 and 100. It’s primarily used to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market, which are indicative of potential trend reversals.
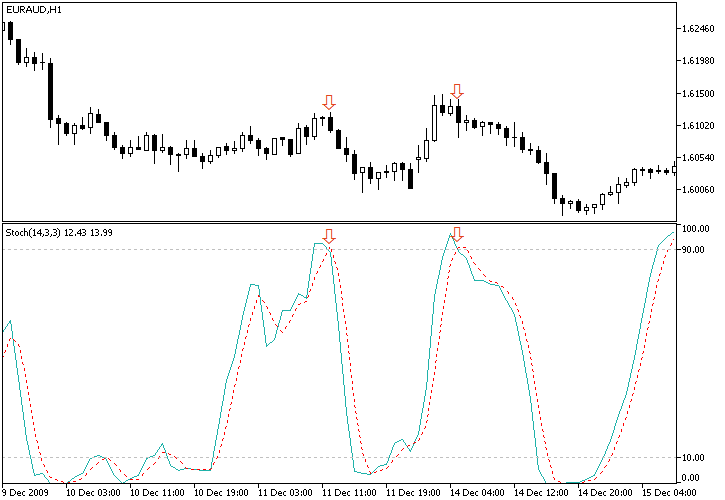
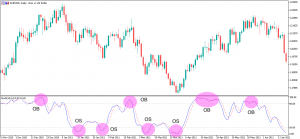
Spotting Overbought and Oversold Conditions
One of the primary roles of the Stochastic Oscillator strategy is to help traders identify overbought and oversold conditions. These conditions suggest that an asset’s price may have deviated too far from its average and could be due for a reversal. In the context of the Stochastic Oscillator Strategy, this is a critical element.
- Overbought Condition: When the Stochastic Oscillator rises above the 80 mark, it indicates that the asset is potentially overbought. Traders using the strategy might interpret this as a signal to consider selling, as a correction or reversal could be on the horizon.
- Oversold Condition: Conversely, when the Stochastic Oscillator drops below the 20 mark, it suggests that the asset is oversold. For traders employing the strategy, this could be seen as an opportunity to consider buying, as the price may be due for a bounce or reversal.
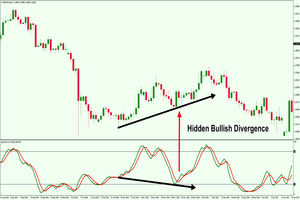
Divergence Analysis
Divergence is another crucial role played by the Stochastic Oscillator. Divergence occurs when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of the indicator. This can be a powerful signal for traders using the Stochastic Oscillator Strategy.
- Regular Divergence: Regular divergence occurs when the price forms a higher high or lower low, while the Stochastic Oscillator does the opposite. For instance, if the price makes a higher high, but the oscillator forms a lower high, it could be a bearish divergence signal, indicating a potential trend reversal to the downside.
- Hidden Divergence: Hidden divergence, on the other hand, happens when the price and the Stochastic Oscillator move in the same direction, but the oscillator leads the price. For example, if the price forms a lower low, but the oscillator creates a higher low, it could be a bullish hidden divergence, suggesting a potential uptrend continuation.
Confirmation and Timing
The Stochastic Oscillator also serves as a confirmation tool in trading strategies. When used in conjunction with other technical indicators or chart patterns, it can help traders refine their entry and exit points. The Stochastic Oscillator Strategy often incorporates these confirmations to increase the reliability of signals.
By understanding the current momentum and potential reversal points indicated by the Stochastic Oscillator, traders can time their trades more effectively. They may wait for the oscillator to move out of overbought or oversold conditions or look for divergence confirmation before executing their trades.
Setting Up the Stochastic Oscillator
In the realm of trading, strategy is everything. And when it comes to developing a robust Stochastic Oscillator strategy, the first step is setting up this powerful technical indicator correctly. In this section, we’ll dive deep into the process of configuring the Stochastic Oscillator, ensuring it becomes a valuable tool in your trading arsenal.
Selecting the Right Trading Platform
Before you can begin setting up the Stochastic Oscillator, you need access to a reliable trading platform. Most popular trading platforms, such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), offer built-in support for this indicator. Ensure you have access to a platform that suits your trading needs.
Launching the Indicator
Once you’re logged into your chosen trading platform, the next step is to locate and launch the Stochastic Oscillator indicator. On most platforms, this can be done by:
- Opening a Price Chart: Begin by opening a price chart for the asset you intend to trade. This could be a currency pair, a stock, a commodity, or any other financial instrument.
- Navigating to Indicators: Look for the “Indicators” or “Studies” menu on your trading platform. Different platforms may use slightly different terminology, but the objective is the same: to access technical indicators.
- Locating Stochastic Oscillator: Within the Indicators menu, search for the Stochastic Oscillator. It’s often listed under the “Oscillators” or “Momentum” category.
- Applying the Indicator: Once you’ve found the Stochastic Oscillator, apply it to your price chart. This action will typically overlay the indicator on your chart, creating two lines – %K and %D.
Configuring Stochastic Oscillator Parameters
The default settings of the Stochastic Oscillator may not always align with your trading strategy or preferences. Customizing the indicator’s parameters is a crucial step in setting it up effectively. Here are the key parameters you can typically adjust:
- %K Period: This parameter determines the number of periods used to calculate the %K line. Common values range from 5 to 14, but you can adjust this based on your trading style and timeframes.
- %D Period: The %D line is often referred to as the signal line. It represents a moving average of the %K line. Like %K, the %D period can be customized to suit your preferences.
- Smoothing: Some platforms offer the option to apply smoothing to the Stochastic Oscillator. Smoothing can help reduce noise in the indicator’s signals.
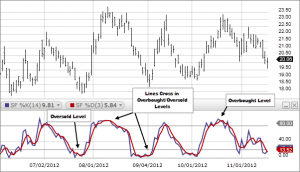
Understanding Overbought and Oversold Levels
One of the primary uses of the Stochastic Oscillator in trading is identifying overbought and oversold conditions. By default, these levels are set at 80 (overbought) and 20 (oversold). However, you can adjust these levels based on your risk tolerance and market conditions.
- Overbought: If you’re trading in a strong uptrend, you may want to adjust the overbought level to a higher value, such as 90 or even 95. This adjustment prevents premature sell signals in robust trends.
- Oversold: Conversely, in a strong downtrend, you can adjust the oversold level to a lower value, like 10 or 15. This modification can help avoid early buy signals when a downtrend is still intact.
Saving Your Settings
Once you’ve customized the Stochastic Oscillator parameters to your liking, it’s essential to save your settings. Most trading platforms allow you to save indicator configurations, making it convenient to apply the same settings to multiple charts or instruments.
Interpreting Stochastic Oscillator Signals
Trading decisions often hinge on interpreting Stochastic Oscillator signals. Understanding how to spot buy and sell signals using %K and %D crossovers is essential. Additionally, we delve into using overbought and oversold conditions as entry and exit points.
Stochastic Oscillator Trading Strategies
The heart of this guide lies in exploring various trading strategies that leverage the Stochastic Oscillator. Whether you’re a day trader, swing trader, or long-term investor, there’s a strategy that can align with your goals. Real-world examples illustrate how traders utilize Stochastic signals to make informed choices.
Benefits and Limitations of the Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator Strategy is a powerful tool that can aid traders in navigating the intricate waters of financial markets. However, like any technical indicator, it comes with its own set of benefits and limitations. Understanding these can be instrumental in effectively integrating the Stochastic Oscillator into your trading strategy.
Benefits of Using the Stochastic Oscillator
- Spotting Overbought and Oversold Conditions: One of the primary advantages of the Stochastic Oscillator is its ability to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market. When %K and %D readings reach extreme levels (usually above 80 for overbought and below 20 for oversold), it signals potential price reversals. Traders can use these signals to make informed decisions about entering or exiting trades.
- Providing Confirmation Signals: The Stochastic Oscillator can be a valuable confirmation tool when used in conjunction with other technical indicators or trading strategies. For example, if a trader identifies a potential trend reversal using a different method, a Stochastic Oscillator signal that aligns with this view can increase the confidence in the trade.
- Divergence Analysis: Divergence occurs when the price of an asset and the Stochastic Oscillator readings move in opposite directions. This can be a powerful signal, indicating a potential change in trend direction. Divergence analysis is a valuable technique that traders can employ with the Stochastic Oscillator.
- Versatility in Timeframes: The Stochastic Oscillator can be applied to various timeframes, from short-term day trading to longer-term investing. This versatility makes it suitable for traders with different trading styles and preferences.
- Simple Interpretation: Unlike some complex technical indicators, the Stochastic Oscillator provides straightforward signals. Traders can quickly grasp the meaning of overbought, oversold, and crossover signals without extensive technical knowledge.
Limitations of the Stochastic Oscillator
- Whipsaws in Choppy Markets: The Stochastic Oscillator can generate false signals, known as “whipsaws,” in choppy or sideways markets. Traders may receive frequent buy and sell signals that do not result in profitable trades during these conditions.
- Lagging Indicator: Like many oscillators, the Stochastic Oscillator is a lagging indicator, meaning it relies on past price data to generate signals. This lag can result in missed opportunities or delayed responses to rapidly changing market conditions.
- Overbought and Oversold Can Persist: In strong trending markets, assets can remain in overbought or oversold conditions for extended periods. Relying solely on these conditions to trigger trades can lead to missed opportunities or premature exits.
- Not Suitable for Trending Markets: The Stochastic Oscillator is primarily designed to identify potential reversals in range-bound markets. It may not perform as well in strongly trending markets where overbought or oversold conditions may persist.
- Subject to False Divergence Signals: While divergence analysis can be powerful, it is not foolproof. False divergence signals can occur, leading to incorrect trading decisions.
Risk Management with the Stochastic Oscillator Strategy
Now, let’s explore how the Stochastic Oscillator Strategy can be integrated into your risk management approach:
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: A fundamental aspect of risk management is setting stop-loss orders. These are predetermined price levels at which you’re willing to exit a trade to limit potential losses. When employing the Stochastic Oscillator strategy, consider placing your stop-loss orders based on the signals generated by the indicator. For example, if you’re going long based on a Stochastic oversold signal, you might set your stop-loss just below the entry point.
- Take-Profit Levels: In addition to stop-loss orders, take-profit levels are equally important. These are predetermined price levels at which you plan to exit a trade to lock in profits. The Stochastic Oscillator can help you identify potential reversal points. When you’re in a winning trade, consider using the Stochastic signals to determine where to set your take-profit levels. This way, you ensure that you exit the trade while the momentum is in your favor.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: A key element of risk management is maintaining a favorable risk-reward ratio. This means that for every trade you take, you should aim for a potential profit that is significantly larger than your potential loss. The Stochastic Oscillator can aid in this by helping you identify entry points with high probability. By using the Stochastic signals to determine entry and exit points, you can calculate and maintain a favorable risk-reward ratio.
- Diversification: Diversifying your trading portfolio is another risk management strategy. While the Stochastic Oscillator can be a valuable tool, it’s not infallible, and there’s always the possibility of false signals. To mitigate this risk, consider spreading your investments across different assets and trading strategies. This way, you reduce your exposure to any single trade or market condition.
- Position Sizing: Determining the appropriate position size is crucial for risk management. The Stochastic Oscillator can help you identify high-probability trade setups. However, it’s essential to adjust your position size based on your risk tolerance and the specific trade’s parameters. If a trade based on Stochastic signals has a higher probability of success, you might consider a larger position size, but always within your risk limits.
Backtesting and Fine-Tuning Strategies
Backtesting is the process of evaluating a trading strategy using historical market data to determine how it would have performed. It allows traders to assess the viability of their Stochastic Oscillator Strategy without risking real capital. Here’s how backtesting contributes to successful trading:
- Performance Validation: Backtesting helps validate the effectiveness of your stochastic oscillator strategy by providing insight into how it would have performed in the past.
- Risk Assessment: It allows traders to assess the risk associated with the stochastic oscillator strategy, including potential drawdowns and losing streaks.
- Parameter Optimization: Traders can fine-tune the parameters of their Stochastic Oscillator Strategy based on historical data to improve its performance.
- Confidence Building: Successful backtesting instills confidence in traders, helping them execute their strategy with discipline and conviction.
The Backtesting Process
Before diving into backtesting, it’s essential to have a clear plan:
- Define Your Strategy: Begin by precisely defining your Stochastic Oscillator Strategy, including entry and exit criteria.
- Select Historical Data: Choose a relevant dataset that aligns with the markets you intend to trade. Ensure the data is of good quality and includes all the necessary details.
- Set Parameters: Configure the parameters of your Stochastic Oscillator indicator in the same way you would in live trading.
- Execute the Strategy: Apply your strategy to the historical data and record the trading decisions it generates.
- Evaluate Results: Analyze the results of your backtest, including profitability, risk-adjusted returns, and drawdowns.
- Iterate and Improve: Use the insights gained from backtesting to fine-tune your strategy. Adjust parameters, risk management rules, or other aspects as needed.
Fine-Tuning Strategies
Fine-tuning involves making adjustments to your Stochastic Oscillator Strategy based on the results of your backtesting. Here’s how you can fine-tune your strategy for optimal performance:
- Optimize Parameters: Use the backtesting results to identify the most effective parameter settings for your Stochastic Oscillator indicator. Adjust the values of variables like the lookback period and smoothing to improve accuracy.
- Refine Entry and Exit Rules: Analyze your historical trades to identify patterns or conditions that can be refined. This could involve tweaking the criteria for entering or exiting trades.
- Enhance Risk Management: Assess your risk management rules, including stop-loss and take-profit levels. Ensure that they align with your risk tolerance and trading objectives.
- Consider Market Conditions: Fine-tune your strategy to adapt to different market conditions. Recognize that what works in a trending market may not be suitable for a ranging market.
- Diversify Assets: If your backtesting reveals that your strategy performs well on multiple assets, consider diversifying your trading portfolio to spread risk.
- Emphasize Discipline: Incorporate the lessons learned from backtesting into your trading discipline. Stick to your strategy and risk management rules consistently.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Trading with the Stochastic Oscillator Strategy can be highly profitable, but it’s not without its challenges. To ensure your success in implementing this strategy, it’s crucial to be aware of and avoid common mistakes that traders often make. In this section, we’ll delve into these pitfalls, offering insights on how to sidestep them and optimize your trading performance with the Stochastic Oscillator strategy.
1. Overlooking Market Context
Mistake: One of the most common errors is neglecting the broader market context when using the Stochastic Oscillator strategy. Traders may focus solely on Stochastic signals without considering factors like overall market trends, economic events, or news releases.
Solution: Always analyze the bigger picture. Incorporate fundamental analysis and market sentiment into your decision-making process. A Stochastic Oscillator strategy should align with the prevailing market conditions for higher probability trades.
2. Using Stochastic Oscillator in Isolation
Mistake: Relying solely on the Stochastic Oscillator without considering other technical indicators can lead to false signals and missed opportunities.
Solution: Combine the Stochastic Oscillator strategy with other indicators such as Moving Averages or Relative Strength Index (RSI) to validate signals. A confirmation from multiple indicators can increase the reliability of your trades.
3. Overtrading
Mistake: Some traders get caught up in the excitement of frequent Stochastic signals, leading to overtrading. This can result in excessive transaction costs and increased risk.
Solution: Be selective in your trades. Only take positions when the Stochastic Oscillator strategy aligns with your overall trading strategy and risk management rules. Quality over quantity should be your mantra.
4. Ignoring Risk Management
Mistake: Neglecting proper risk management is a grave error. Traders may not set stop-loss orders or take-profit levels, exposing themselves to significant losses.
Solution: Always implement risk management measures. Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit levels to secure profits. Ensure your risk-to-reward ratio is favorable for each trade.
5. Chasing Overbought/Oversold Signals
Mistake: Novice traders often make the mistake of buying immediately when the Stochastic Oscillator strategy indicates oversold conditions or selling when it’s overbought. However, markets can remain in these states for extended periods.
Solution: Wait for a confirmation signal before acting on overbought or oversold conditions. Look for other technical indicators or price patterns to validate the trade setup.
6. Neglecting Divergence Signals
Mistake: Divergence signals, where the Stochastic Oscillator strategy disagrees with price action, are valuable but are sometimes overlooked.
Solution: Pay close attention to divergence signals, as they can indicate potential trend reversals. Regularly scan for these signals in your analysis.
7. Lack of Backtesting and Strategy Evaluation
Mistake: Trading without backtesting your Stochastic Oscillator strategy can be a costly mistake. Traders may not know how their strategy performs under different market conditions.
Solution: Conduct thorough backtesting to assess the historical performance of your Stochastic Oscillator strategy. Evaluate its strengths and weaknesses and make necessary adjustments.
8. Emotional Trading
Mistake: Emotional reactions, such as fear and greed, can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive decisions based on Stochastic signals.
Solution: Stick to a predefined trading plan and rules. Embrace discipline and avoid emotional trading by setting clear entry and exit criteria.
9. Neglecting Education
Mistake: Jumping into Stochastic Oscillator strategy without a deep understanding of the indicator and its nuances can lead to suboptimal results.
Solution: Invest time in learning and practicing with the Stochastic Oscillator strategy. Read books, take courses, and stay updated on market conditions.
10. Overconfidence
Mistake: Overestimating your abilities and the accuracy of the Stochastic Oscillator strategy can lead to unwarranted risks.
Solution: Maintain a humble and realistic approach. Acknowledge that losses are part of trading, even with a sound strategy.
Conclusion
The Stochastic Oscillator Strategy offers a versatile approach to trading, catering to traders of all levels and risk appetites. By understanding its intricacies and deploying it effectively, you can make more informed trading decisions and navigate the markets with greater confidence.