Introduction
Option trading strategies play a crucial role in the financial markets, providing traders with a range of tools to capitalize on market opportunities and manage risk. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various option trading strategies, covering directional strategies, volatility strategies, income-generation strategies, hedging techniques, and advanced strategies. By understanding these strategies, traders can enhance their decision-making process and potentially achieve greater success in the world of options.
Basic Concepts of Options Trading
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s essential to grasp the basic concepts of options trading. Options are financial derivatives that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified time frame. Options have intrinsic value (the difference between the strike price and the current market price) and time value (reflecting the potential for the option to gain more value before expiration). Several factors influence option pricing, including the underlying asset, strike price, volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates.
Directional Option Trading Strategies
Directional option trading strategies are a category of option trading strategies that aim to profit from anticipated price movements in the underlying asset. These strategies allow traders to take a specific view on whether the price will rise (bullish) or fall (bearish), providing opportunities for potential gains in both upward and downward trending markets. Let’s explore some popular option trading strategies that can be implemented based on market expectations.
Long Call and Long Put Options
One of the simplest directional strategies is buying long call or long put options. A long call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, within a specific time frame. Traders typically buy long call options when they expect the price of the underlying asset to rise significantly, utilizing these option trading strategies to profit from potential price increases.
Conversely, a long put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price within a specific time frame. Traders typically buy long put options when they anticipate a significant decline in the price of the underlying asset, utilizing these option trading strategies to profit from potential price decreases.
Covered Call and Covered Put Options
Covered call and covered put options are strategies that involve owning the underlying asset while simultaneously selling call or put options against it. These option trading strategies are often used when traders have a neutral or slightly bullish or bearish outlook on the underlying asset.
In a covered call strategy, traders sell call options against their existing stock holdings. By selling the call options, traders receive a premium, generating additional income. If the price of the underlying asset remains below the strike price at expiration, the options expire worthless, and traders keep the premium collected. If the price exceeds the strike price, traders may be obligated to sell the stock at the strike price but still benefit from the premium received. Covered call options are popular among income-generating option trading strategies.
Similarly, in a covered put strategy, traders sell put options against their existing stock holdings. By selling the put options, traders receive a premium, generating additional income. If the price of the underlying asset remains above the strike price at expiration, the options expire worthless, and traders keep the premium collected. If the price falls below the strike price, traders may be obligated to purchase the stock at the strike price, but the premium received helps offset the cost. Covered put options are another example of option trading strategies that generate income.
Bullish and Bearish Vertical Spreads
Bullish and bearish vertical spreads involve simultaneously buying and selling options with different strike prices but the same expiration date. These option trading strategies aim to capitalize on price movements within a specific range.
A bullish vertical spread, also known as a bull spread, consists of buying a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously selling a call option with a higher strike price. The goal is to profit from an expected increase in the underlying asset’s price while limiting potential losses. The premium received from selling the higher strike call helps offset the cost of buying the lower strike call. Bullish vertical spreads are examples of option trading strategies used in anticipation of upward price movements.
Conversely, a bearish vertical spread, also known as a bear spread, involves buying a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously selling a put option with a lower strike price. Traders utilize this strategy when they anticipate a decline in the price of the underlying asset. The premium received from selling the lower strike put helps offset the cost of buying the higher strike put. Bearish vertical spreads are examples of option trading strategies employed in anticipation of downward price movements.
Volatility Option Trading Strategies
Option trading strategies play a vital role in navigating volatile markets. These strategies provide traders with a toolkit to capitalize on price fluctuations and manage risk effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various option trading strategies that are particularly suited for volatile market conditions. By understanding and implementing these strategies, traders can potentially profit from increased market volatility while mitigating potential risks.
Understanding Volatility and Its Impact on Options
Volatility is a measure of the price fluctuations observed in the market. During periods of high volatility, prices can swing dramatically, presenting both opportunities and risks for traders. When it comes to options, volatility is a crucial factor that influences their pricing. Higher volatility generally leads to higher option premiums, reflecting the increased probability of larger price swings. Conversely, lower volatility tends to result in lower option premiums.
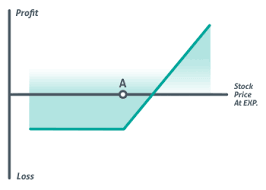
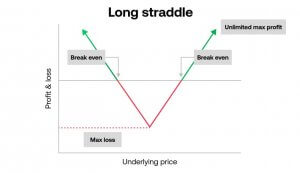
Long Straddle: Profiting from Significant Price Swings
The long straddle is an option trading strategy designed to profit from significant price movements, regardless of their direction. This strategy involves buying both a call option and a put option on the same underlying asset, with the same expiration date and strike price. By owning both options, traders can potentially benefit from substantial price swings. The long straddle is particularly suitable when expecting high volatility, as it allows traders to profit from large price movements.
Long Strangle: Maximizing Profitability with a Wider Range
Similar to the long straddle, the long strangle is an option trading strategy employed when expecting significant price movements. However, unlike the long straddle, the long strangle involves buying a call option and a put option with different strike prices. This strategy provides traders with a wider range of profitable outcomes, as the options’ strike prices are set further from the current market price. The long strangle is an excellent choice when anticipating high volatility but being uncertain about the direction of the price movement.
Short Straddle: Capitalizing on Range-Bound Markets
The short straddle is an option trading strategy utilized when expecting low volatility and a relatively stable price range. This strategy involves selling both a call option and a put option on the same underlying asset, with the same expiration date and strike price. By selling options, traders can collect premiums, aiming for both options to expire worthless. The short straddle is most profitable in range-bound markets, where the price remains relatively stable.
Short Strangle: Limited Risk in Low-Volatility Environments
The short strangle is similar to the short straddle in that it aims to profit from low volatility. However, the short strangle involves selling a call option and a put option with different strike prices. This strategy is employed when traders expect the underlying asset’s price to remain range-bound. Like the short straddle, the short strangle allows traders to collect premiums. However, the risk is limited to the difference between the strike prices. The short strangle is most effective when the price remains within the selected strike prices.
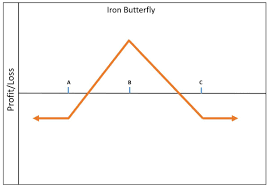
Butterfly Spreads: Capitalizing on Specific Price Ranges
Butterfly spreads are option trading strategies designed for a specific price range and anticipated low volatility. This strategy involves simultaneously buying an “inside” option and an “outside” option, while also selling two options at a strike price in between. The butterfly spread’s risk/reward profile is unique, offering potential profitability when the price settles near the middle strike price at expiration. Butterfly spreads are most effective when expecting limited price movement within a predetermined range.
Iron Condors: Profiting from Range-Bound Markets with Limited Risk
Iron condors are option trading strategies designed for range-bound markets with limited price movement. This strategy combines a bear call spread (selling a call option with a lower strike price and buying a call option with a higher strike price) and a bull put spread (selling a put option with a lower strike price and buying a put option with a higher strike price). Iron condors allow traders to collect premiums while limiting potential losses through the purchase of out-of-the-money options. This strategy is most effective when the underlying asset’s price remains within a specific range.
Considerations and Risk Management in Volatile Markets
When employing option trading strategies in volatile markets, it is crucial to consider several factors. Proper risk management is paramount. Traders must define their risk tolerance, establish appropriate position sizing, and implement stop-loss levels. Regular monitoring of market conditions and adjustments to the strategies may be necessary to adapt to changing volatility levels.
Income-Generating Option Trading Strategies
Generating consistent income is a primary objective for many traders. Fortunately, the options market offers several option trading strategies specifically designed to generate income. These income-generating option trading strategies involve leveraging options contracts to generate premiums, which can potentially provide a steady cash flow. Let’s explore some popular income-generating strategies.
Cash-Secured Put Writing: Cash-Secured Put Writing is an income-generating option trading strategy that involves selling put options while setting aside sufficient cash to cover the potential purchase of the underlying asset at the strike price. This option trading strategy is suitable when the trader has a bullish or neutral outlook on a particular stock or security. By selling put options, the trader collects the premium upfront and commits to buying the underlying asset at the strike price if the options are exercised. If the options expire worthless, the trader keeps the premium as profit.
For instance, suppose an investor believes XYZ stock is a solid investment at the current price of $50 per share. They can sell a cash-secured put option with a strike price of $45 and an expiration of one month, receiving a premium of $2 per share. If the stock remains above $45 at expiration, the options expire worthless, and the trader keeps the premium. However, if the stock price falls below $45, the trader is obligated to purchase the shares at that price using the reserved cash.
Covered Call Writing: Covered Call Writing is another popular income-generating option trading strategy that involves selling call options against an existing stock position. This option trading strategy is employed when the trader has a neutral or slightly bearish outlook on a stock. By selling call options, the trader collects premiums and grants the buyer the right to purchase the shares at the strike price within a specified time frame. If the stock price remains below the strike price at expiration, the options expire worthless, and the trader keeps the premium as profit while retaining ownership of the shares.
For example, let’s say an investor owns 100 shares of ABC stock, currently trading at $60 per share. They sell one call option contract with a strike price of $65 and an expiration of one month, receiving a premium of $2 per share. If the stock price remains below $65 at expiration, the options expire worthless, and the trader keeps the premium. However, if the stock price rises above $65, the trader may be required to sell their shares at the strike price.
Iron Condors for Income: Iron Condors are multi-leg option trading strategies that can be employed to generate income in sideways or range-bound markets. This option trading strategy involves selling out-of-the-money call and put options while simultaneously buying further out-of-the-money call and put options for protection. The goal is for the underlying asset to remain within a specific price range until expiration, allowing the trader to collect the premiums from the sold options.
To illustrate, suppose a trader believes XYZ stock will remain range-bound between $50 and $60. They can sell an out-of-the-money call option with a strike price of $60 and an out-of-the-money put option with a strike price of $50. Simultaneously, they purchase a call option with a strike price of $65 and a put option with a strike price of $45 for protection. By selling the options closer to the current stock price, the trader collects higher premiums. If the stock price stays between $50 and $60 at expiration, all options expire worthless, and the trader keeps the premiums.
Using Option Trading Strategies for Income Generation: These income-generating option trading strategies can provide traders with regular cash flow while potentially mitigating downside risks. However, it’s important to understand the associated risks and market conditions. Proper risk management is crucial to protect against adverse movements in the underlying asset or unexpected market events. Traders should also be aware of the potential for assignment or exercise of options and have a plan in place to manage such scenarios.
Hedging Strategies with Options
Hedging is an essential risk management technique that involves offsetting potential losses in one position by taking an opposite position in another instrument or asset. Options provide an effective tool for hedging purposes due to their flexibility and ability to limit downside risk. In this section, we will explore various hedging strategies that utilize options as a means of protecting existing positions or portfolios.
One common hedging strategy is using option trading strategies for protective puts. This strategy involves purchasing put options on an underlying asset to provide insurance against potential price declines. By holding a long position in the underlying asset and a corresponding long put option, traders can limit their downside risk. If the price of the asset drops, the put option gains value, offsetting the losses in the underlying position. Protective puts are particularly useful for investors who have unrealized gains in a stock but want to protect against a potential downturn.
Another popular hedging strategy is the collar strategy, which combines the purchase of put options and the sale of call options. This strategy is often used by investors who hold a long position in an asset and want to protect against potential losses while still generating income. By purchasing put options, they limit their downside risk. Simultaneously, by selling call options, they generate income but cap their potential profits if the asset’s price rises above the strike price of the call options.
The married put strategy is another effective hedging technique within the realm of option trading strategies. This strategy involves buying put options as a form of insurance for an existing stock position. It offers downside protection while allowing for potential upside gains. By purchasing put options, traders can limit their potential losses if the stock price declines, as the put option gains value. However, if the stock price rises, they can still participate in the upside potential.
These hedging strategies with options provide traders and investors with a degree of protection against adverse price movements. By utilizing options as insurance, market participants can mitigate risk without necessarily needing to exit their existing positions. This flexibility is one of the primary advantages of options in hedging strategies.
It’s important to note that while hedging can protect against downside risk, it also comes with associated costs. Option premiums, transaction costs, and the potential limitation of profits are factors that traders should consider when implementing hedging strategies. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully analyze the risk-reward dynamics and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of option trading strategies within the context of one’s overall investment objectives.
Advanced Option Trading Strategies
When it comes to option trading, mastering advanced strategies can elevate your trading skills to the next level. These advanced option trading strategies provide experienced traders with additional flexibility and potential profit opportunities in the ever-evolving market. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various advanced option trading strategies, highlighting their unique characteristics and how they can be used to enhance profits. So, let’s explore these powerful strategies and discover how they can take your trading game to new heights.
Understanding the Power of Advanced Option Trading Strategies
Advanced option trading strategies are designed to capitalize on complex market scenarios and provide traders with a diverse range of tools to manage risk and maximize profits. By incorporating these advanced strategies into your trading arsenal, you can potentially unlock new profit opportunities that go beyond the traditional directional and volatility strategies.
1. Ratio Spreads: Amplifying Your Potential
Ratio spreads are advanced option trading strategies that allow you to amplify your profit potential or limit potential losses by using an uneven number of long and short options. With ratio spreads, you can take advantage of asymmetrical risk/reward profiles to capitalize on specific market conditions and price expectations. By incorporating ratio spreads into your trading strategy, you can optimize your potential gains while effectively managing risks.
2. Synthetic Positions: Replicating Underlying Assets
Synthetic positions are advanced option trading strategies that replicate the risk/reward characteristics of owning an underlying asset. By combining options and/or stock positions, synthetic positions offer a flexible and cost-effective alternative to directly owning the underlying asset. With synthetic positions, you can gain exposure to specific stocks or market indexes while efficiently managing risk. Incorporating synthetic positions into your trading approach expands your trading opportunities and allows you to capitalize on market movements.
3. Calendar Spreads: Profiting from Time Decay
Calendar spreads, also known as horizontal spreads or time spreads, are advanced strategies that enable you to profit from time decay, also known as theta decay. By simultaneously buying and selling options with different expiration dates, you can take advantage of the differing rates of time decay between near-term and longer-term options. Calendar spreads offer an opportunity to generate consistent income or benefit from anticipated price movements within a specific time frame. Integrating calendar spreads into your trading strategy allows you to harness the power of time decay for increased profitability.
4. Diagonal Spreads: Combining Flexibility and Strategy
Diagonal spreads are advanced option trading strategies that combine elements of both vertical and horizontal spreads. These strategies involve buying and selling options with different strike prices and expiration dates. With diagonal spreads, you gain a high degree of flexibility to tailor your risk/reward profiles based on your market outlook. By selecting strike prices and expiration dates that align with your specific expectations, you can strategically manage risk and capture potential profits. Diagonal spreads empower you to take advantage of anticipated price movements and time decay simultaneously.
Maximizing Success with Advanced Option Trading Strategies
To maximize your success with advanced option trading strategies, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the underlying principles, associated risks, and potential rewards. Thoroughly analyze market conditions, evaluate volatility levels, and consider the impact of time decay. Stay informed about market news, economic events, and earnings announcements that may influence the prices of the underlying assets.
Implementing proper risk management techniques and continuously monitoring your positions are vital. Regularly assess your trades, be prepared to make necessary adjustments or exit positions when market conditions change, and always adhere to your predefined trading plan.
Risk Management and Trade Adjustments
Effective risk management and the ability to make timely trade adjustments are crucial elements of successful option trading strategies. Traders must proactively protect their capital and adapt to changing market conditions. In this section, we will delve into the importance of risk management, explore various risk management techniques, and discuss the process of making trade adjustments to optimize option positions within the context of option trading strategies.
The Significance of Risk Management
Option trading involves inherent risks, including the potential loss of capital. Implementing a robust risk management strategy is essential to protect against adverse market movements and preserve capital for future trades. Risk management helps traders set predetermined levels of acceptable risk, define their maximum loss thresholds, and ensure disciplined decision-making.
Within the context of option trading strategies, risk management revolves around two primary aspects: position sizing and risk-reward ratios. Properly sizing positions based on account size and risk tolerance is crucial to maintain a diversified portfolio and prevent overexposure to any single trade. Additionally, evaluating the risk-reward ratio of each trade helps assess potential profitability and aligns with overall trading objectives.
Risk Management Techniques in Option Trading Strategies
- Setting Stop Loss Orders: Stop loss orders are predetermined price levels at which a trade is automatically closed to limit potential losses. By setting stop loss orders, traders can effectively manage risk and protect their capital in case the market moves against their position.
- Utilizing Trailing Stops: Trailing stops adjust dynamically as the market moves in favor of the trade, locking in profits and protecting against potential reversals. This technique allows traders to let their winning trades run while providing a safety net against sudden price reversals.
- Diversification and Asset Allocation: Diversifying option trading strategies across different underlying assets, sectors, or strategies can help mitigate risks. By spreading trades across multiple assets, traders reduce the impact of a single trade’s adverse outcome on their overall portfolio.
- Defining Maximum Loss Thresholds: Before entering a trade, determining the maximum acceptable loss for each position is crucial. This ensures that losses are kept within predefined limits and prevents emotionally driven decisions during adverse market conditions.
- Implementing Risk-Reward Analysis: Evaluating the risk-reward ratio of each trade before execution helps assess the potential profitability. Trades with a favorable risk-reward ratio have the potential for higher rewards relative to the potential risk, aligning with the trader’s objectives.
Trade Adjustments in Option Trading Strategies
Trade adjustments refer to the process of modifying existing option positions in response to changing market conditions. Making timely adjustments allows traders to optimize risk exposure, potentially enhance profitability, or reduce potential losses. Here are a few common trade adjustment techniques used in option trading strategies:
- Rolling Options Positions: Rolling involves closing an existing option position and simultaneously opening a new position with different parameters. Traders can roll options positions forward in time (calendar roll) or to a different strike price (vertical roll) to adjust to changing market expectations.
- Adjusting Strike Prices: When the underlying asset’s price approaches the strike price of an option, traders may consider adjusting the strike price to maintain a favorable risk-reward profile. This adjustment can involve rolling the position to a higher or lower strike price to align with new market conditions.
- Changing the Number of Contracts: Adjusting the number of contracts in a position allows traders to increase or decrease exposure to a specific option strategy. Scaling into or out of positions can help manage risk, capitalize on favorable market movements, or minimize losses.
- Implementing Protective Strategies: Protective strategies, such as buying additional options to hedge against potential losses or reduce risk exposure, can be utilized when the market moves against a position. These strategies aim to limit downside risk and protect capital.
- Trade Exits and Cut Losses: Sometimes, the best adjustment is to exit a trade entirely. If a position is consistently underperforming or the original thesis is invalidated, traders may choose to cut losses and exit the trade to preserve capital for better opportunities.
Developing a Trading Plan and Executing Option Strategies
A well-defined trading plan is the foundation for successful option trading strategies. It provides structure, discipline, and a clear roadmap for executing trades. By developing a trading plan tailored to individual goals, risk tolerance, and preferred option trading strategies, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve overall trading performance.
Importance of a Trading Plan
Having a trading plan is essential for several reasons. First, it helps traders maintain consistency and discipline in their option trading strategies. A well-structured plan outlines specific entry and exit criteria, risk management rules, and trade execution guidelines, allowing traders to execute their strategies with precision. By adhering to a well-defined plan, traders can avoid impulsive decisions based on emotions or market noise.
Second, a trading plan facilitates effective risk management. It helps traders identify their risk tolerance and define maximum acceptable losses. With proper risk management techniques in place, traders can protect their capital and minimize potential losses. This is especially crucial when dealing with complex financial instruments like options.
Components of a Trading Plan
A comprehensive trading plan for executing option trading strategies should include the following components:
1. Goals and Objectives
Define clear, realistic trading goals and objectives related to option trading strategies. These can include profit targets, percentage returns, or consistent income generation. By setting specific goals, traders can measure their progress and align their efforts accordingly.
2. Risk Management
Identify and assess personal risk tolerance in relation to option trading strategies. Determine the maximum amount of capital to risk per trade or per day. Implement position-sizing techniques, such as allocating a specific percentage of capital to each trade or using fixed dollar risk limits. Additionally, define stop-loss levels and establish rules for trailing stops or adjusting positions as the trade progresses. Effective risk management is vital in option trading strategies to protect against potential losses and preserve capital.
3. Selection of Option Trading Strategies
Select and specify the option trading strategies to be employed based on personal preferences, risk tolerance, and market conditions. This can include directional strategies like long calls or long puts, volatility strategies such as straddles or strangles, income-generation strategies like covered calls, or a combination of multiple strategies. The chosen strategies should align with the trader’s goals and risk profile.
4. Entry and Exit Criteria
Define clear entry and exit criteria for each option trade. Entry criteria may include specific technical indicators, chart patterns, or fundamental factors that signal favorable conditions for the selected strategy. Exit criteria should consider profit targets, stop-loss levels, or predefined criteria for adjustments or trade management based on changing market conditions. Having predetermined entry and exit criteria helps traders make objective decisions and reduces emotional biases.
5. Trade Execution
Establish guidelines for executing trades related to option trading strategies. Determine whether to use limit orders or market orders, and specify the maximum percentage or dollar amount of capital to allocate to each trade. Clear guidelines for trade execution ensure consistency and help traders achieve optimal trade fills.
6. Trade Monitoring and Evaluation
Outline a process for monitoring trades and evaluating performance in option trading strategies. Determine the frequency of reviewing positions, tracking progress, and making adjustments as necessary. Regularly assess trade outcomes and review the effectiveness of the selected strategies to identify areas for improvement. Ongoing evaluation is crucial in refining option trading strategies and optimizing overall performance.
Executing Option Trading Strategies
Once a trading plan is in place, executing option trading strategies involves implementing the defined rules and guidelines. Here are some key points to consider when executing option trading strategies:
1. Research and Analysis
Thoroughly research the underlying asset, market conditions, and any factors that may impact the selected option trading strategy. Conduct technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential opportunities and assess risk. Stay informed about the latest news and developments relevant to the chosen strategies.
2. Risk and Position Sizing
Apply risk management principles defined in the trading plan to option trading strategies. Determine the appropriate position size based on risk tolerance and capital allocation guidelines. Avoid risking an excessive amount of capital on any single trade. Proper position sizing helps manage risk and maintain a balanced portfolio.
3. Order Placement
Place orders based on the defined entry and exit criteria in option trading strategies. Use appropriate order types (limit orders, stop orders, or market orders) to execute trades efficiently. Double-check order details to ensure accuracy before submitting them. Accurate order placement is crucial to achieving desired trade fills.
4. Trade Monitoring
Regularly monitor open positions to stay informed about market developments and evaluate the ongoing performance of the trades related to option trading strategies. Pay attention to changes in price, volatility, or any relevant news that may require adjustments or trade management. Effective trade monitoring allows for timely decision-making and proactive management of option positions.
5. Adjustments and Trade Management
Be prepared to make necessary adjustments to option positions if market conditions change or the original assumptions prove incorrect. This may involve rolling options positions, adjusting strike prices, or changing the number of contracts to adapt to new information. Proactive trade management helps optimize trade outcomes and maximize potential profits while minimizing risk.
6. Trade Record-Keeping
Maintain accurate records of all option trades related to the selected strategies, including entry and exit dates, strike prices, premiums, and any adjustments made. This record-keeping enables traders to analyze and evaluate the effectiveness of their option strategies over time. It also helps with tax reporting and compliance requirements.
Conclusion
Option trading strategies offer a wide array of tools and techniques for traders to capitalize on market opportunities and manage risk effectively. By understanding the various strategies outlined in this comprehensive guide and adapting them to individual trading goals and market conditions, traders can gain a competitive edge in the options market. Continuous learning, practice, and disciplined execution are key to mastering these strategies and achieving success in options trading.